☺POSSESSIVE PRONOUNS☺
CONCEPT BASIC
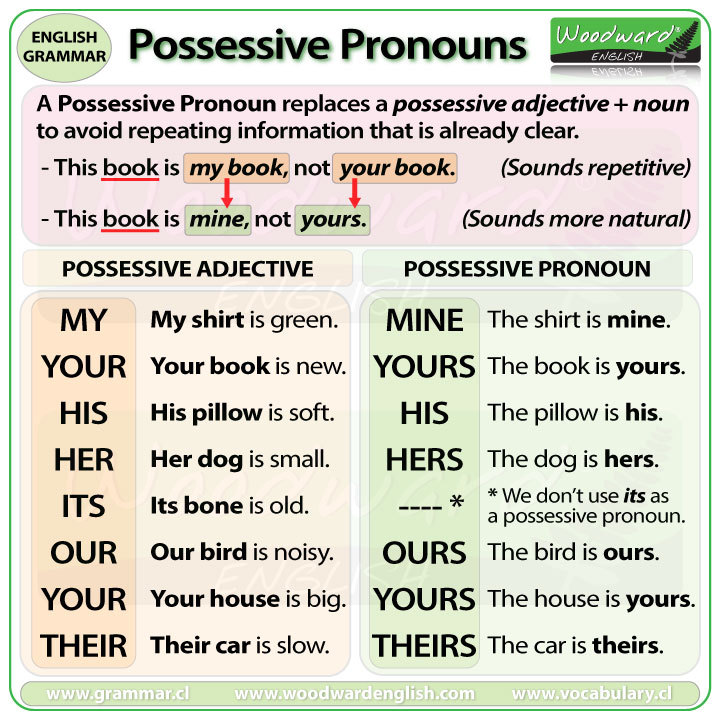
Possessive pronouns are used in English to avoid repeating information that is already clear. In general it makes the sentence less confusing because the same information is not being repeated.
This book is my book, not your book. (Sounds repetitive)
This book is mine, not yours. (Mine and yours are possessive pronouns)
In the sentence, mine is a possessive pronoun that replaces my book.
In the sentence, yours is a possessive pronoun that replaces your book.
Possessive pronouns are used in English to avoid repeating information that is already clear. In general it makes the sentence less confusing because the same information is not being repeated.
This book is my book, not your book. (Sounds repetitive)
This book is mine, not yours. (Mine and yours are possessive pronouns)
In the sentence, mine is a possessive pronoun that replaces my book.
In the sentence, yours is a possessive pronoun that replaces your book.
•BASIC RULES•
* We avoid using the possessive pronoun ITS.
Examples:
Of yours
It is also very common to say a friend/some friends + of + possessive pronouns.
Both of these sentences are correct and both common in English.
Yours faithfully - Yours sincerely
Yours is also used in English with faithfully or sincerely at the end of a formal letter or e-mail. The two common expressions are:
COMPLEMENTATION
📹: Here is a video to complement this lesson
EXERCISES
| - Select the correct answer. 1. He’s got telephone number, but I haven’t got his. 2. car is much faster than . 3. We went to a disco with Stephanie, Terry and some friends of . 4. I hate her! She’s no friend of . 5. Is this bag or ? |